In a matter of no time, serverless architecture AWS has turned into a major option for developers and startups, even though it has been comparatively a little time. It removes the burden of taking care of the infrastructure and thus, teams can only focus on coding and delivering value as quickly as possible. AWS offers such great services as Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB that they handle the difficult tasks silently under the surface, whether you are launching an API, doing real-time analytics, or streamlining the workflow.
You pay only for what you consume and have the freedom to deploy features without any concern about resource provision being too much or too little. That level of removal of the system’s complexities is a fantastic advantage for fast development and cost control.
Of course, as with any technology strategy, serverless comes with trade-offs. Cold starts, restricted run time, and vendor lock-in are all legitimate issues that teams need to balance against the payoffs. In this article, we are going to reveal the main advantages of AWS serverless, discuss the cases where it is the best option and analyse the drawbacks that might surprise you if you are not careful.
What is the Functioning of AWS Lambda in a Serverless Environment?
It executes the corresponding code instantly and at high speed in response to different events such as HTTP requests, changes in the database, uploads of files, scheduled events, etc. Lambda functions are stateless; thus, they are triggered, and then they scale according to the user demand without any human intervention.
AWS Lambda Use cases are examples of building a distributed architecture that includes S3, DynamoDB or API Gateway. The triggering of the upload of an object to S3 activates a Lambda function to perform media processing, image resizing, or user input validation, among others. The very short interval from event generation to code execution gives the opportunity to apply a variety of dynamic use cases across different sectors.
A current use of AWS Lambda that is definitely a nice one is the creation of fast applications like chatbots, IoT backends, or data processing pipelines, where instant execution and high efficiency are necessities. AWS Lambda is a perfect fit for projects that are limited in budget yet still require rapid scalability, flexibility, and low latency. This is mainly due to the fact that it only bills for the actual execution time consumed.
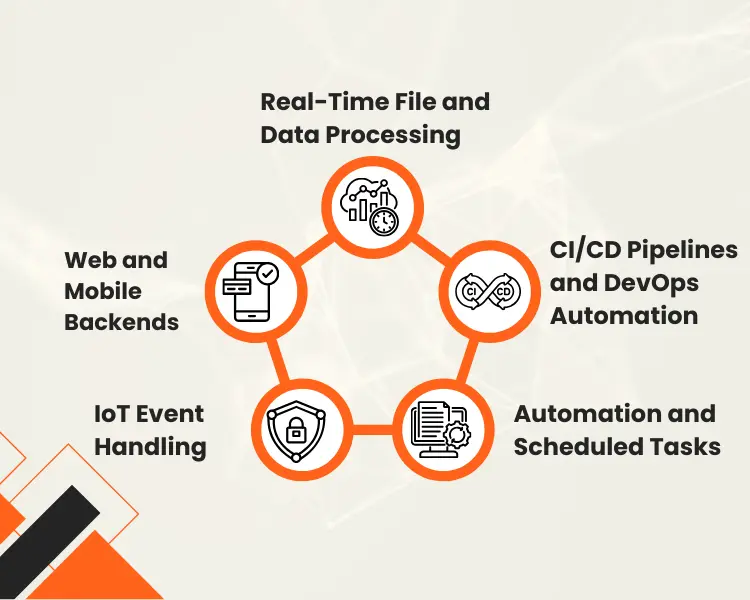
Which Serverless Architecture Apps are Best Fit on AWS?
Serverless architecture is best for event-driven workloads, which are highly scalable and need almost no management of infrastructure. Below, we give you a detailed discussion about the kinds of applications that are most favoured for this:
1. Real-Time File and Data Processing
The usage of serverless functions for auto-resizing images, cleansing data streams, or changing file formats is the best option. This is used extensively in media, analytics, and automation, where the input-output occurs continuously and has to be processed in real-time. Serverless pros and cons have to be weighed thoroughly here for processing speed and cost.
2. Web and Mobile Backends
Serverless architectures not only make the creation of minimal REST APIs easier but also the user authentication processes. If API Gateway and DynamoDB are used together, the developers can very easily build a back-end for both mobile and web apps that are scalable without worrying about the scaling of backends.
3. IoT Event Handling
IoT gadgets and sensors give off events that can be easily activated through Lambda functions. The serverless setup is ideal for such applications in which the backend activities, like metric storage or alert systems, are triggered by device communication at regular intervals.
4. Automation and Scheduled Tasks
Using Lambda, apps can take advantage of time-determined triggers through Amazon EventBridge or CloudWatch that include actions like sending email notifications, cleaning up the database, etc. Implying developers’ lives to be so easy, the ones who are comfortable with running scripts for specific tasks would not have to start up instances.
5. CI/CD Pipelines and DevOps Automation
Using functions enables performing the logic of build, test, and deployment in CI/CD pipelines. Activities such as checking code quality, unit testing, or validating infrastructure are being done efficiently, thus increasing agility in deployments.
What Role Does Serverless Play in Building Microservices?
Serverless represents one of the top technologies for microservices and the idea of independent deployable units. A microservices architecture is made up of different services, each responsible for a particular business function and provided with minimal APIs for communication between the services. Serverless models such as AWS Lambda give developers an easy and flexible means to deploy numerous functional services without incurring the costs associated with setting up dedicated infrastructures for each service.
Microservices would have meant the deployment of multiple containers or VMs in the past, which would turn operations into a complex scenario due to the different kinds of issues involved, like scaling, patching, and resource allocation, to mention a few. For example, the product catalogue management service may have a much larger number of users during the holiday season as compared to the billing service, which would not experience any increase in usage during that time.
Serverless Conductor AWS not only liberates the development teams from the overload of infrastructure issues but also lets them direct their efforts entirely towards business logic, roll out features more often, and make more iterations. Moreover, serverless services connect without any difficulty to monitoring, logging, and security tools, therefore, granting the required visibility and control to handle microservices in a large-scale setting.
How do Serverless Applications Benefit from Built-in High Availability?
The cloud vendor’s premises regarding availability and fault tolerance allow the user not to make any server provisioning or operation at all, thus enjoying a great benefit. This indicates that the application is not just functional but also operating at full capacity regularly, even when there are no users or during a complete infrastructure shutdown.
It is a standard practice that any Lambda function is deployed in at least three different Availability Zones (AZs), therefore minimising the probability to almost non-existent that a failure will happen at any single point. The users of these functions will remain oblivious to the failure due to AWS’s seamless automatic rerouting and failover processes.
Programmers do not have to design elaborate disaster recovery schemes, as there is resilience built in. The continuous operation of these applications is so important that the feature is perfectly suited for such applications. In an FaaS deployment, the developers do not have to handle any errors manually; their replication and load balancing are all handled automatically.
What Testing Approaches Are Suitable for Serverless Environments?
Serverless testing can be rather hard towards the functions that are distributed and event-based, but testing strategically makes applications reliable. The following are some of the powerful tactics:
- Unit Testing for Functions- Every single Lambda function cocoon has its own unique business logic to be dealt with.
- End-to-End (E2E) Testing- It copies the flowworks of all the applications. Cypress or Postman is used by the testing team to check user flows in such a way that the whole microservice flow operates as expected.
- Load Testing- It tests the performance of functions when there is high concurrency. Tools like Artillery or Gatling can detect performance bottlenecks and thus help in the cold start or memory allocation optimisation process.
- Error Simulation & Recovery Testing- It performs service failures simulations to examine error handling procedures, retries, and fallbacks. This is very important for the validation of SLAs in Microservices running on AWS.
Conclusion
Serverless architecture AWS allows programmers to create applications that can handle large volumes, run fast, and still be economical by removing the need to deal with server management, scaling issues, and fault tolerance. Serverless implementation has simplified and reduced the cost of developing real-time data processing, workflow automation, and microservices.
Revolution AI knows how to create and deliver production-ready serverless applications that are the strongest ones and meet the company’s needs at their best. Our experts, who are proficient in employing Lambda, API Gateway, DynamoDB, and other resources, offer a warranty for trouble-free deployment, outstanding performance, and enormous scalability to business people.
Frequently Asked Questions
Serverless architecture represents a form of cloud computing where developers manage their applications without needing support from the basic infrastructure.
The biggest benefits are the automatic scalability, payment solely according to what has been used, having high availability as a standard feature, quicker time-to-market for applications, and low operating expenses.
Sure, a few of the downsides would be cold start latency, maximum execution time (for Lambda), distributed service debugging complexity, and the risk of vendor lock-in.
AWS implements a heavy-duty security system that includes IAM roles, VPC integration, encryption, and continuous monitoring of CloudTrail and CloudWatch.
Serverless is not a viable option for tasks that require long-running processes, scheduled deployments.

Hemal Sehgal
Introducing Hemal Sehgal, a talented and accomplished author with a passion for content writing and a specialization in the blockchain industry. With over two years of experience, Hemal Sehgal has established a strong foothold in the writing world, c...read more